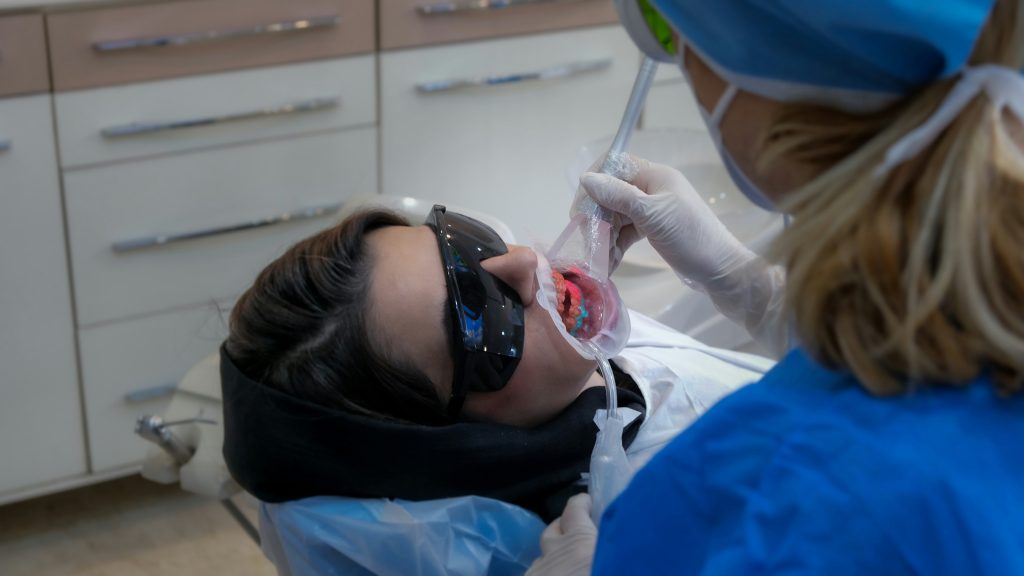
If you’re expecting and notice a small lump or swelling on your gums, you might wonder how to get rid of cyst on gums safely without risking your baby’s health. Gum cysts during pregnancy are fairly common, often caused by hormonal changes and heightened gum sensitivity. While they can look alarming, most cysts are treatable with simple, dentist-approved methods that prioritise both maternal comfort and oral hygiene. This guide explains what gum cysts are, why they appear more frequently during pregnancy, and—most importantly—how to remove or manage them safely. You’ll also find expert advice on home care, professional treatment, and ways to keep your gums healthy throughout every trimester.
What Is a Gum Cyst and Why It Appears During Pregnancy
When you’re expecting, your body undergoes extraordinary hormonal and physiological changes that can affect not only your overall well-being but also your oral health. One of the more unexpected side effects may be the development of a gum cyst—a small, fluid-filled lump that appears along the gum line or between teeth. Understanding how to get rid of cyst on gums safely starts with learning what causes them, why they appear more frequently during pregnancy, and how they differ from other oral swellings.
Understanding the Nature of Gum Cysts
A gum cyst, also called a dental cyst or gingival cyst, forms when soft tissue around a tooth becomes inflamed or blocked, often as a result of infection or trapped debris. These cysts can contain fluid, pus, or air depending on the underlying issue. They typically appear as small round bumps, sometimes tender, and may vary in colour from pale pink to red. While minor cysts can resolve naturally, untreated infections may worsen, requiring a dentist’s attention to prevent pain or swelling from spreading.
Why Gum Cysts Are More Common During Pregnancy
Pregnancy triggers substantial hormonal fluctuations—especially in oestrogen and progesterone. These hormones increase blood circulation to gum tissues, making them softer, more sensitive, and prone to inflammation. Coupled with morning sickness, altered eating habits, and fatigue that may affect brushing routines, bacteria can build up quickly along the gum line. The result is a higher likelihood of developing gum cysts or pregnancy gingivitis.
According to a study in the Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, hormonal changes can intensify the body’s inflammatory response to dental plaque, leading to swelling and cyst formation. This makes oral hygiene and timely dental assessments especially important during pregnancy.
Types of Gum Cysts You Might Encounter
Not all gum cysts are the same. Identifying the type helps your dentist determine the safest and most effective pregnancy-compatible treatment plan.
| Type of Gum Cyst | Typical Cause | Common Symptoms | Treatment Considerations (Pregnancy-Safe) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gingival Cyst | Blocked salivary glands or minor trauma | Small, painless bump on the gum surface | Often resolves naturally; maintain gentle brushing and salt-water rinses |
| Periapical (Root) Cyst | Infection from untreated tooth decay | Pain, swelling, or pus discharge | Requires dentist evaluation; antibiotics or safe drainage under local supervision |
| Periodontal Cyst | Chronic inflammation or deep tartar buildup | Swollen gums, tenderness, bad breath | Professional cleaning and careful monitoring |
Source: Journal of Clinical Periodontology and NCBI Oral Health Data, 2024.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
In early stages, gum cysts are often painless, which can make them easy to ignore. During pregnancy, however, hormonal changes may accelerate irritation or infection. You should contact your dentist promptly if you notice:
- Persistent swelling or a lump on your gums
- Discomfort or bleeding while brushing
- Pus discharge or an unpleasant taste
- Swelling that worsens or spreads to nearby tissue
These symptoms could indicate that a cyst has become infected or that another oral condition is developing. Pregnant women in Singapore are advised to keep up regular dental check-ups and professional cleaning. HealthHub (Health Promotion Board) specifically encourages having your teeth cleaned and regularly examined during pregnancy, while SingHealth states that routine dental care is safe in pregnancy when appropriately performed. Non-urgent procedures are often scheduled in the second trimester for comfort, as reflected in public-health guidance for parents in Singapore (see Families for Life, which draws on HPB material).
How Gum Cysts Differ from Other Oral Conditions
It’s easy to mistake gum cysts for ulcers or minor irritations caused by brushing. However, cysts are typically firm, persistent, and may contain fluid or pus, unlike mouth ulcers that heal within a week. Understanding these differences is key to knowing how to get rid of cyst on gums safely and effectively, without resorting to self-treatment or unverified home remedies.
The Link Between Gum Health and Pregnancy Outcomes
Although gum cysts are localized, untreated infections may elevate overall inflammation in your body. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, advanced gum disease (periodontitis) in pregnant women has been associated with poorer pregnancy outcomes such as preterm birth and low birth weight. The precise mechanism remains under investigation, but the correlation underscores the importance of maintaining good oral health throughout pregnancy. This makes oral hygiene more than just a cosmetic concern—it’s part of holistic prenatal care. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, using alcohol-free mouthwash, and maintaining a nutrient-rich diet with calcium and vitamin D can all support gum health and lower inflammation risk.
By understanding what gum cysts are, why they develop, and how pregnancy hormones play a role, you’re already better prepared to protect your smile during this important time. The next section will guide you through five safe, dentist-approved ways to get rid of a gum cyst during pregnancy, combining gentle home care and professional strategies to keep both you and your baby healthy.
5 Safe Dentist-Approved Ways to Get Rid of a Gum Cyst During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can make your gums more sensitive than usual. If you develop a gum cyst, even a small one, you might feel discomfort, swelling, or a strange pressure around your teeth. The good news is that you can manage this safely with a combination of professional care and gentle home remedies. These first three steps focus on what you can do every day to soothe irritation, lower inflammation, and prevent infection — all while keeping your baby safe. Understanding how to treat swollen gums while pregnant starts with these foundational habits.
1. Rinse with Warm Salt Water for Gentle Cleansing
Warm salt-water rinses are among the simplest yet most effective ways to relieve pain and swelling caused by gum cysts. Salt acts as a natural antiseptic and helps reduce bacteria in the mouth without using chemicals or alcohol. Mix half a teaspoon of salt into a glass of warm water, swish gently around your mouth for about 30 seconds, and spit it out. This rinse soothes inflammation, promotes healing, and discourages bacterial growth near the affected area.
For best results, repeat this rinse two or three times daily, especially after meals. Avoid using overly hot water, which can irritate gums.Research indicates that during pregnancy, hormonal changes can increase gum inflammation and bleeding. Studies have not specifically confirmed that saline rinsing during pregnancy directly improves healing, but clinical research supports salt-water rinses as a safe, gentle way to soothe inflammation and aid recovery after dental care. Regular rinsing helps reduce bacteria and gum swelling, especially for expectant mothers who experience pregnancy gingivitis. According to the Mayo Clinic, using a warm salt-water rinse can naturally ease irritation and promote oral comfort.
While formal trials of simple saline rinses during pregnancy are limited, rinsing with a mild salt-water solution is widely recognised as a safe, low-risk method to soothe inflamed gums and reduce bacterial load in the mouth (general post-operative oral care literature supports this). Thus, you may consider adding a gentle salt-water rinse to your routine during pregnancy, but be aware it’s supportive rather than a proven treatment for serious gum disease..
2. Brush with Care — Technique and Tools Matter
During pregnancy, your gums are more vascular, meaning they bleed more easily. Aggressive brushing or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can make things worse. Choose a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush with small, circular motions rather than forceful horizontal strokes. Use fluoride toothpaste twice a day to strengthen enamel and help control bacterial plaque around the cyst area. Electric toothbrushes with pressure sensors are also a good choice because they prevent overbrushing.
If you experience bleeding, switch to a toothpaste formulated for sensitive gums. Avoid whitening or charcoal-based toothpaste, which can irritate already delicate gum tissues. Don’t forget to clean your tongue gently, as bacteria there can migrate to your gum line and worsen inflammation.
3. Schedule a Professional Dental Cleaning at the Right Time
If the cyst doesn’t subside with good home care, professional cleaning is often necessary. Dental scaling and polishing are safe during pregnancy when performed with proper precautions. The second trimester is usually the best time for elective procedures since morning sickness tends to lessen and your baby’s major organs have already developed.
During the procedure, your dentist removes tartar and plaque from below the gum line — a key step to controlling infection and promoting healing. In Singapore, both dental and maternal-health professionals agree that routine scaling and polishing are safe during pregnancy when performed with appropriate precautions. The Leong Dental Clinic notes that scaling can be done safely at any stage of pregnancy, especially when adrenaline-free anaesthetics are used. Similarly, SmartParents Singapore advises that maintaining oral cleanliness through professional scaling helps reduce gum bleeding and swelling, which are common during pregnancy. This simple, preventive visit not only keeps your gums comfortable but can also help prevent recurring cysts and inflammation later in pregnancy.
| Safe Treatment | Main Benefit | Safety During Pregnancy | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warm Salt-Water Rinse | Natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory action | Completely safe at all stages | 2–3 times daily |
| Soft-Bristled Brushing | Reduces gum trauma and bleeding | Safe daily habit | Twice daily |
| Professional Cleaning | Removes deep tartar and bacteria | Safe under dentist supervision (2nd trimester preferred) | Once per trimester if needed |
While home care and cleaning go a long way, some gum cysts require additional support to heal properly. This second part explores targeted treatments, dietary adjustments, and warning signs that indicate when you should see a dentist immediately. Each step helps you understand how to treat swollen gums while pregnant using safe, evidence-based methods.
4. Use Medications and Mouth Rinses Approved for Pregnancy
If your gum cyst becomes painful or infected, your dentist may prescribe specific treatments that are safe for pregnancy. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) remains the preferred pain reliever, but avoid ibuprofen and aspirin during the later stages of pregnancy. For bacterial control, dentists often recommend chlorhexidine mouthwash (0.12%)—a clinically proven antiseptic that targets plaque and inflammation without systemic absorption.
In Singapore, most dentists recommend using this rinse for 7–10 days, twice daily after brushing. If you experience persistent discomfort, topical gels containing mild herbal or glycerin bases can provide extra relief. Always check that your mouth rinse is alcohol-free and fluoride-safe, as certain over-the-counter formulas can cause dryness or irritation.
Dentists may use local anaesthetics, including lidocaine with or without epinephrine, during pregnancy, and routine dental care — including the administration of local anaesthetic — is considered safe at any stage. This is stated in the American Dental Association guidance on pregnancy, which also notes that delaying necessary treatment can worsen problems. Likewise, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists affirms that dental X-rays with shielding and local anaesthesia such as lidocaine, with or without epinephrine, are safe during pregnancy. Together, these recommendations mean that dental work required to remove infection or perform drainage can be completed comfortably and safely while you are pregnant.
5. Support Gum Healing Through Nutrition and Hydration
Healthy gums need proper nutrition to heal. Vitamin C helps repair tissue, while calcium and vitamin D maintain strong bone and tooth structure. Include foods like citrus fruits, spinach, broccoli, tofu, milk, and fortified soy alternatives. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish or flaxseed also have anti-inflammatory benefits that can support gum healing. Try to maintain a balanced diet with smaller, frequent meals if nausea affects your appetite.
Hydration is equally crucial. Dehydration can cause dry mouth, reducing saliva flow that protects against bacteria. According to Singapore’s Health Promotion Board and its HealthHub portal, most adults are advised to drink about six to eight glasses of water a day; and those who are pregnant, perspiring heavily or living in humid climates are encouraged to increase their fluid intake accordingly. Carry a water bottle throughout the day, and limit caffeinated beverages that can dehydrate you.
When to Seek Immediate Dental Attention
Although mild cysts usually heal within one to two weeks, you should contact your dentist immediately if you notice:
- Persistent pain or pressure that worsens after a few days
- Swelling that spreads to your cheek or jaw
- Bleeding or pus coming from the gum area
- Fever, fatigue, or difficulty opening your mouth
These symptoms may indicate an abscess or deeper infection that requires immediate drainage or antibiotics. Dentists in Singapore typically collaborate with obstetricians to ensure all medications prescribed are pregnancy-safe. Prompt care not only prevents complications but also helps restore comfort quickly.
Long-Term Gum Care for Pregnant Women
Once your cyst has healed, preventive care remains the best protection. Continue using fluoride toothpaste, brush and floss daily, and schedule routine check-ups after delivery. Consider switching to a water flosser for easier cleaning between teeth if you experience gum sensitivity. Regular monitoring allows your dentist to identify early gum changes before they turn into cysts or infections.
By following these five dentist-approved methods, you can confidently manage gum cysts and maintain a healthy smile throughout pregnancy. With proper care, understanding how to treat swollen gums while pregnant becomes more than symptom control, it’s about creating a foundation for lasting oral wellness for both you and your baby.
Risks of Ignoring a Gum Cyst While Pregnant
When you are expecting, your body undergoes hormonal and immune system changes that can affect your oral health. A gum cyst—a small fluid-filled bump on the gums—might seem minor at first, but during pregnancy, ignoring it can lead to serious complications for both you and your baby. Understanding the potential risks helps you take prompt action and avoid preventable dental and pregnancy-related issues.
1. Increased Risk of Gum Infection and Abscess Formation
Pregnancy hormones like progesterone and estrogen increase blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to swelling. When a gum cyst becomes infected, it can rapidly develop into an abscess—a pocket of pus that may cause pain, bleeding, and facial swelling. Hormonal changes during pregnancy make your gums softer and more prone to bleeding and infection. These conditions, if left untreated, can progress from gingivitis to more serious gum disease that affects gum tissue and bone support. In advanced cases, the infection can require more invasive treatment because your body’s immune responses and healing are altered during pregnancy.
A similar local source points out that untreated gum disease in pregnancy is associated with increased risk of complications like pre-term birth and low birth weight, as maternal inflammation and bacterial spread may impact overall health.
2. Possible Association with Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight
There is growing evidence that severe gum disease during pregnancy may be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that periodontal disease in expectant mothers has been linked to higher risks of preterm birth and low birth weight. Although the precise biological mechanism remains under study, inflammation and oral bacteria may trigger systemic responses that affect the placenta and fetal growth. For this reason, regular dental check-ups and early treatment of gum cysts are strongly encouraged.
3. Pain and Difficulty Eating or Maintaining Nutrition
A painful cyst can make it difficult for you to chew, brush, or floss properly, leading to poor nutrition and suboptimal oral hygiene. During pregnancy, your nutritional needs increase—particularly for calcium, vitamin D, and protein. The Health Promotion Board Singapore notes that a balanced diet supports both maternal and fetal health. If dental pain prevents you from eating properly, it could impact your baby’s nutrient supply, making timely dental care even more important.
4. Bacterial Transmission and Systemic Inflammation
Untreated cysts can harbour bacteria that enter the bloodstream, potentially leading to bacteremia. In severe cases, systemic infection could affect organs such as the heart or kidneys. While such cases are rare, they are preventable with professional care. A guideline from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) reassures that dental treatments and cleanings, including the use of local anaesthetics like lidocaine, are safe during pregnancy when properly administered. This means that addressing infections early is both safe and essential.
5. Emotional Stress and Impact on Pregnancy Wellness
Chronic oral pain or visible gum swelling can increase anxiety, disrupt sleep, and add stress—factors known to influence overall pregnancy well-being. Emotional distress can also raise cortisol levels, which have been associated with negative pregnancy outcomes in some studies. By addressing gum cysts early, you safeguard not only your oral health but also your peace of mind during this important stage of life.
Summary of Key Risks and Recommendations
| Risk Factor | Potential Consequence | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated infection | Abscess, tooth loss, systemic spread | Seek dental treatment promptly |
| Severe gum disease | Possible link to preterm birth or low birth weight | Regular dental check-ups |
| Poor oral hygiene due to pain | Nutritional deficiency, increased caries risk | Gentle brushing, dentist-guided cleaning |
| Bacterial spread | Systemic inflammation or rare infection | Safe dental procedures with anaesthetic if required |
Ignoring a gum cyst while pregnant is not just a dental issue, it’s a health risk that can affect your comfort, nutrition, and pregnancy outcomes. Regular check-ups with your dentist, gentle home care, and early intervention are the safest ways to protect both your smile and your baby’s well-being.
Manage Gum Problems Safely During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can heighten your risk of gum problems due to hormonal changes, increased blood flow, and shifts in your immune response. These changes may cause gum swelling, tenderness, or even lead to a gum cyst. Understanding how to manage these conditions safely ensures you protect both your oral health and your baby’s well-being. In Singapore, where humid weather and dietary habits can affect oral care, following dentist-approved methods helps you control gum issues effectively.
How to Heal a Cyst on Your Gums?
When you notice a small lump or swelling on your gum, you may wonder how to heal a cyst on your gums safely. The first step is maintaining excellent oral hygiene. Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and use a soft-bristled toothbrush to reduce irritation. Rinse with warm saltwater — mix ½ teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water — to help ease inflammation. While these steps can soothe symptoms, most gum cysts won’t disappear entirely without professional dental care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirms that dental treatments, including cleanings and local anaesthesia, are safe during pregnancy when administered under supervision.
How to Deal with Gum Problems During Pregnancy?
Knowing how to deal with gum problems during pregnancy helps prevent complications like gum infections and abscesses. Consistent dental cleaning and check-ups are key. The HealthHub Singapore advises that professional cleaning is safe and recommended at any stage of pregnancy. Floss gently to remove plaque between teeth, and avoid harsh mouth rinses with alcohol. Additionally, maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamin C, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids — these nutrients help repair gum tissue and prevent cyst recurrence. Hydration is equally essential; aim for at least six to eight glasses of water daily, as advised by the Health Promotion Board Singapore.
Can Gum Cysts Go Away Naturally?
Many expectant mothers ask whether gum cysts can go away naturally. In mild cases, minor swelling might subside as hormonal levels stabilise, but cysts caused by infection or blocked glands often persist. Avoid trying to pop or drain them at home, as this increases infection risk. Instead, observe whether the swelling lasts more than a week, causes pain, or begins to discharge. If any of these occur, it’s time to see a professional. The American Dental Association (ADA) confirms that routine dental procedures, including scaling, fillings, and local anaesthetics like lidocaine, are safe during pregnancy.
When to See a Dentist for a Gum Cyst During Pregnancy
Understanding when to see a dentist for a gum cyst during pregnancy can prevent further infection or discomfort. You should seek professional evaluation if you experience persistent swelling, severe pain, or bleeding. Dentists in Singapore are trained to manage pregnancy-safe treatments, from cleaning and drainage to prescribing antibiotics if necessary. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), both dental X-rays and anaesthetics such as lidocaine (with or without epinephrine) are considered safe when performed by licensed professionals. Most dentists prefer scheduling non-urgent treatments in the second trimester for comfort.
Summary of Safe Gum Care Practices During Pregnancy
| Practice | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Brush and floss regularly | Reduce plaque buildup and prevent cyst formation |
| Rinse with warm saltwater | Ease gum swelling and soothe inflammation |
| Eat balanced meals rich in calcium and vitamin C | Support gum healing and strengthen oral tissue |
| Schedule safe dental visits | Early detection and treatment of gum cysts |
Managing gum problems safely during pregnancy requires consistent care, a balanced diet, and professional supervision. Most dental treatments are safe when performed correctly, so don’t hesitate to consult your dentist if you experience discomfort. Taking proactive steps to treat gum cysts or inflammation ensures you stay healthy — and gives your baby the best start possible.
Preventing Gum Cysts During Pregnancy: Tips for Long-Term Gum Health
Pregnancy can make your gums more vulnerable to inflammation, bleeding, and small swellings known as gum cysts. These oral changes are primarily caused by increased hormones like progesterone and estrogen, which heighten sensitivity to plaque and bacteria. By adopting preventive strategies early, you can avoid discomfort and safeguard your long-term gum health throughout pregnancy and beyond. Here’s how to maintain a healthy smile safely in Singapore’s humid climate and ensure both you and your baby stay well.
1. Keep Up a Consistent Oral Care Routine
Good daily hygiene is your first defence against gum cysts. Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and use a soft-bristled toothbrush to protect sensitive gum tissue. Floss once daily to remove plaque between teeth. According to HealthHub Singapore, routine professional cleaning is safe at any stage of pregnancy and helps control bacteria that can cause gum inflammation. If your gums bleed slightly while brushing, do not stop — gentle cleaning prevents plaque build-up that could lead to cyst formation.
2. Schedule Regular Dental Check-Ups During Pregnancy
Do not postpone your dental visits simply because you are expecting. The American Dental Association (ADA) confirms that routine dental care, including X-rays with protection and the use of local anaesthetics such as lidocaine, is safe for pregnant women. Schedule at least one check-up per trimester to monitor your gum condition and detect any cysts early. If you are prone to gum swelling or bleeding, inform your dentist so that your cleaning procedure can be adjusted for comfort.
3. Adopt a Gum-Friendly Pregnancy Diet
Your diet plays a major role in preventing gum cysts during pregnancy. The Health Promotion Board Singapore encourages pregnant women to eat foods rich in calcium, vitamin C, and protein to maintain strong teeth and gum tissue. Include green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, yogurt, and lean meats in your meals. Limit sugar and processed snacks that can trigger bacterial growth and increase cyst risk. Drink six to eight glasses of water daily , or more if you live in a humid environment, to support saliva production, which naturally cleanses your mouth.
4. Manage Hormonal Changes with Gentle Care
Pregnancy hormones can cause gum tissue to react strongly to plaque, leading to redness and small nodules that may evolve into cysts. Use alcohol-free mouthwash or saltwater rinses to soothe irritation. Mix half a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and rinse twice daily to control bacteria safely. If you notice recurring gum cysts despite good care, see your dentist promptly for evaluation. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that oral infections in pregnancy can be treated safely when managed early and under professional supervision.
5. Avoid Self-Medicating or Ignoring Symptoms
It may be tempting to ignore a small gum lump or take over-the-counter remedies, but self-treatment can worsen the issue. Never apply painkillers or herbal pastes directly to your gums without consulting a healthcare professional. If your gum cyst becomes painful or starts to discharge, book an appointment immediately. Dentists in Singapore can safely drain cysts, perform deep cleaning, and prescribe antibiotics suitable for pregnancy. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) confirms that dental procedures, including local anaesthesia, pose minimal risk when done by qualified professionals.
Summary of Preventive Gum Care During Pregnancy
| Preventive Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Brush and floss daily | Remove plaque and reduce cyst formation |
| Visit the dentist every trimester | Monitor gum changes and treat early issues |
| Eat a nutrient-rich diet | Strengthen gums and improve resistance to infection |
| Rinse with warm saltwater | Soothe inflammation and balance oral bacteria |
| Avoid self-treatment | Prevent complications and ensure safety for baby |
By following these tips for long-term gum health, you can prevent gum cysts and other oral problems during pregnancy safely. Consistent hygiene, professional monitoring, and balanced nutrition go a long way toward maintaining a healthy smile. Pregnancy is the perfect time to invest in preventive care, protecting your oral health today supports your overall well-being for years to come.
Conclusion
Taking care of your gums during pregnancy is more than a matter of comfort, it’s an important part of protecting your overall health and your baby’s development. Hormonal changes, morning sickness, and changes in eating habits can all make your gums more prone to swelling, bleeding, and cyst formation. However, by maintaining regular dental check-ups, following a balanced diet, and practising gentle but consistent oral hygiene, you can greatly reduce these risks. Safe dental treatments, including professional cleaning and the use of local anaesthetics such as lidocaine, have been proven effective and safe for expectant mothers when administered correctly. Whether you’re managing an existing gum cyst or looking to prevent new ones, timely attention and guidance from your dentist make all the difference. Remember, gum health and pregnancy health are closely connected, healthy gums help support a healthy pregnancy. Stay proactive, listen to your body, and never hesitate to seek dental care when something feels off. A confident smile and strong gums will carry you comfortably through pregnancy and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. Is pregnancy gingivitis dangerous?
Pregnancy gingivitis is common among expectant mothers, but it can become serious if left untreated. Hormonal changes increase blood flow to the gums, making them more prone to swelling, bleeding, and infection. If neglected, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, which has been linked to potential complications such as preterm birth or low birth weight. The good news is that pregnancy gingivitis can be safely managed with regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental check-ups.
2. How to get rid of a tooth abscess without going to the dentist while pregnant?
It’s not advisable to treat a tooth abscess at home during pregnancy. While warm saltwater rinses and maintaining good oral hygiene can help reduce pain and inflammation, they cannot remove the infection. A tooth abscess requires professional treatment to prevent it from spreading and affecting your overall health. Dentists can safely treat abscesses during pregnancy using approved medications and anaesthetics that do not harm your baby.
3. Can gum cysts go away on their own during pregnancy?
Some gum cysts may shrink as hormone levels stabilise, but most do not fully disappear without dental care. Ignoring a cyst can lead to infection or discomfort. Your dentist can safely drain or treat the cyst using pregnancy-friendly methods. Regular dental visits throughout your pregnancy help detect these issues early and prevent complications.
4. Are dental treatments and anaesthetics safe during pregnancy?
Yes, most dental treatments and local anaesthetics are safe during pregnancy when performed by a qualified professional. Procedures such as cleaning, fillings, and treatment for infections can be done safely, especially in the second trimester. Always inform your dentist about your pregnancy so they can tailor the treatment to your needs.
5. How can I prevent gum cysts and infections while pregnant?
Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss regularly, and rinse with warm saltwater to keep bacteria under control. Eat foods rich in vitamin C and calcium to strengthen your gums, and drink plenty of water throughout the day. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are key to preventing gum cysts and maintaining oral health during pregnancy.
References:
- American Dental Association. “Pregnancy.” ADA – Oral Health Topics. July 14, 2025.
https://www.ada.org/resources/ada-library/oral-health-topics/pregnancy - Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. “Talking to Pregnant Women About Oral Health.” May 15, 2024.
https://www.cdc.gov/oral-health/hcp/conversation-tips/talking-to-pregnant-women-about-oral-health.html - Thomson Medical. “Dental Checkup During Pregnancy: What You Need to Know.” October 9, 2024.
https://www.thomsonmedical.com/blog/dental-care-during-pregnancy/ - Ashford Dental Centre (Singapore). “Oral Health Tips for Pregnant Women.” November 7, 2024.
https://ashforddentalcentre.com.sg/oral-health-tips-for-pregnant-women/ - BigSmile Dental Clinic (Singapore). “Dental Care During Pregnancy: What You Need to Know.” June 21, 2024.
https://www.bigsmile.com.sg/dental-care-during-pregnancy-what-you-need-to-know/ - American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). “Oral Health Care During Pregnancy and Through the Lifespan.” August 2013 (Reaffirmed 2025).
https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2013/08/oral-health-care-during-pregnancy-and-through-the-lifespan - “Oral Health During Pregnancy – 2025.” Journal of Midwifery & Women’s Health. March 20, 2025.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jmwh.13752
Related Post:
The Science of Enamel Remineralization: 2026 Guide to Modern Preventive Dentistry
Deep Teeth Cleaning vs. Regular Cleaning: Singaporean Perspective in 2026